In this article we ll walk you through the basics of heat sinks and heat sink design including the calculations involved in defining the proper heat sink for your application.
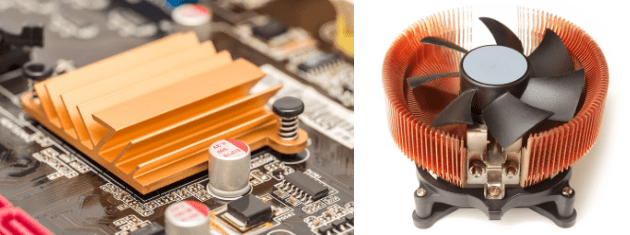
Active heat sink design.
Heat sinks are most commonly utilized in active passive or hybrid configurations.
Passive heat sinks rely on natural convection meaning the buoyancy of hot air alone causes the airflow generated across the heat sink system.
An active heat sink uses an electronic device s power supply to connect to a fan or a peltier device to actively divert heat away from the components by circulating air to cool the component or conduct heat away from it.
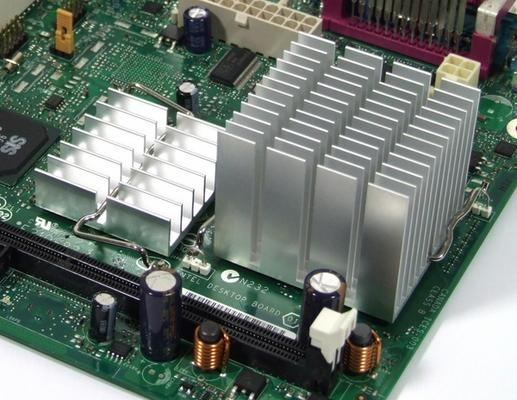
A heat sink also commonly spelled heatsink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium often air or a liquid coolant where it is dissipated away from the device thereby allowing regulation of the device s temperature.
Remember that sometimes active heat sinks are required for enhanced heat dissipation.
Active heat sinks are often used in conjunction with passive heat sinks.
These systems are advantageous as they do not require secondary power or.
Heat sinks help absorb and dissipate the heat generated by electronic devices.
In computers heat sinks are used to cool cpus gpus and some chipsets and ram modules.
Passive heat sinks have no.
Heat sinks are used on a broad range of electronics ranging from cpus to motor drivers.
The heatsink is typically a metallic part which can be attached to a device releasing energy in the form of heat with the aim of dissipating that heat to a surrounding fluid in order to prevent the device overheating.